原文:Using CORS
Introduction | 介绍
APIs are the threads that let you stitch together a rich web experience. But this experience has a hard time translating to the browser, where the options for cross-domain requests are limited to techniques like JSON-P(which has limited use due to security concerns) or setting up a custom proxy (which can be a pain to set up and maintain).
API 是让你将丰富的 web 体验拼接在一起的纽带。但是在过去,跨域请求被限制只能在一些技术上使用的时候,例如 JSON-P(出于安全考虑,使用上有诸多限制)或者设置自定义代理(难于设置和维护),这些体验是很难在浏览器中实现的。
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a W3C spec that allows cross-domain communication from the browser. By building on top of the XMLHttpRequest object, CORS allows developers to work with the same idioms as same-domain requests.
跨源资源共享 (CORS)是一个 W3C 规范,允许浏览器跨域通信。建立在 XMLHttpRequest 对象之上,CORS 允许开发者使用与同域请求相同的语法。
The use-case for CORS is simple. Imagine the site alice.com has some data that the site bob.com wants to access. This type of request traditionally wouldn’t be allowed under the browser’s same origin policy. However, by supporting CORS requests, alice.com can add a few special response headers that allows bob.com to access the data.
CORS 的用例非常简单。想象一下网站 alice.com 上有一些网站 bob.com 想要获取的数据。这种类型的请求在浏览器的同源策略下通常不会被允许的。然而,通过支持 CORS 请求,alice.com 可以增加一些特殊的响应头来允许 bob.com 获取数据。
As you can see from this example, CORS support requires coordination between both the server and client. Luckily, if you are a client-side developer you are shielded from most of these details. The rest of this article shows how clients can make cross-origin requests, and how servers can configure themselves to support CORS.
正如你在上面的例子中看到的,支持 CORS 需要服务端与客户端之间的协作。幸运的是,如果你是以为客户端开发者,你已经被屏蔽了大部分细节。本文其他部分将会阐述如何让客户端发起跨域请求,以及如何配置服务器来支持 CORS。
Making a CORS Request | 发起一个 CORS 请求
This section shows how to make a cross-domain request in JavaScript.
本节展示如何用
JavaScript发起跨域请求
Creating the XMLHttpRequest object | 创建一个XMLHttpRequest 对象
CORS is supported in the following browsers:
下面这些浏览器支持了 CORS:
- Chrome 3+
- Firefox 3.5+
- Opera 12+
- Safari 4+
Internet Explorer 8+
(see the complete list of supported browsers at http://caniuse.com/#search=cors )
(查看浏览器支持的完整列表: http://caniuse.com/#search=cors )
Chrome, Firefox, Opera and Safari all use the XMLHttpRequest2 object. Internet Explorer uses the similar XDomainRequest object, which works in much the same way as its XMLHttpRequest counterpart, but adds additional security precautions.
Chrome, Firefox, Opera and Safari 全部使用 XMLHttpRequest2 对象。Internet Explorer 使用的是类似的 XDomainRequest 对象,它与 XMLHttpRequest 对应部分的工作方式大致相当,但是增加了额外的安全防范措施。
To get started, you will first need to create the appropriate request object. Nicholas Zakas wrote a simple helper method to help sort out the browser differences:
首先,你需要创建适当的请求对象。Nicholas Zakas 写了一个简单的 helper 方法来帮助检查理清浏览器间的差异。
1 | function createCORSRequest(method, url) { |
Event handlers | 事件处理程序
The original XMLHttpRequest object had only one event handler, onreadystatechange, which handled all responses. Although onreadystatechange is still available, XMLHttpRequest2 introduces a bunch of new event handlers. Here is a complete list:
原始的 XMLHttpRequest 对象只有一个事件处理程序,
onreadystatechange,这个处理程序处理了所有的返回。但是onreadystatechange仍然可用,XMLHttpRequest2 引入了一堆新的事件处理程序。这里是一个完整列表:
| Event Handler | Description |
|---|---|
| onloadstart* | When the request starts. 当请求开始的时候 |
| onprogress | While loading and sending data. 当加载和发送数据的时候 |
| onabort* | When the request has been aborted. For instance, by invoking the abort() method. 当请求被中止的时候。例如通过调用 abort() 方法。 |
| onerror | When the request has failed. 当请求失败的时候 |
| onload | When the request has successfully completed. 当请求成功完成的时候。 |
| ontimeout | When the author specified timeout has passed before the request could complete. 当请求完成之前达到了作者设定的超时时间的时候。 |
| onloadend* | When the request has completed (either in success or failure). 当请求完成(不论成功或者失败)的时候 |
* starred items are not supported by IE’s XDomainRequest
*星号标记的项目是不被 IE 浏览器的 XDomainRequest 对象支持的。
source: http://www.w3.org/TR/XMLHttpRequest2/#events
For most cases, you will at the very least want to handle the onload and onerror events:
多数情况下,你至少要处理
onload和onerror事件:
1 | xhr.onload = function() { |
Browers don’t do a good job of reporting what went wrong when there is an error. For example, Firefox reports a status of 0 and an empty statusText for all errors. Browsers also report an error message to the console log, but this message cannot be accessed from JavaScript. When handling onerror, you will know that an error occurred, but not much else.
浏览器在出现错误时不能很好地定位错误来源。例如,Firefox 对所有错误都报告一个状态 0 和空的
statusText。浏览器也会在控制台日志中报告错误,但是这种错误信息不能被JavaScript获取。当处理onerror的时候,你只知道发生了错误,但是除此之外没有更多信息了。
withCredentials
Standard CORS requests do not send or set any cookies by default. In order to include cookies as part of the request, you need to set the XMLHttpRequest’s .withCredentials property to true:
标准的 OCRS 请求默认不发送也不设置任何cookie缓存。为了将 cookie 缓存作为请求的一部分,你需要设置 XMLHttpRequest的
.withCredentials属性为 true:
1 | xhr.withCredentials = true; |
In order for this to work, the server must also enable credentials by setting the Access-Control-Allow-Credentials response header to “true”. See the server section for details.
为了使之生效,服务端也必须通过设置
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials响应头为 ”true” 来允许证书(credentials)。更多细节看这里 server section 。
1 | Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true |
The .withCredentials property will include any cookies from the remote domain in the request, and it will also set any cookies from the remote domain. Note that these cookies still honor same-origin policies, so your JavaScript code can’t access the cookies from document.cookie or the response headers. They can only be controlled by the remote domain.
.withCredentials属性将包含来自请求中远程域的任何 cookie 缓存,并且还将设置来自远程域的任何 cookie 缓存。注意这些缓存仍然遵循同源策略,所以你的 JavaScript 代码访问 document.cookie 中的 cookie 缓存,或者响应头(response headers)。它们只能被远程域名控制。
Making the request | 发起请求
Now that your CORS request is configured, you are ready to make the request. This is done by calling the send() method:
CORS 请求配置完成后,你就可以发起请求了。这是通过调用
send()方法来完成的。
1 | xhr.send(); |
If the request has a body, it can be specified as an argument to send().
如何请求有一个请求体,请求体可以被声明为
send()方法的一个参数。
And thats it! Assuming the server is properly configured to respond to CORS requests, your onload handler will fire with the response, just like the standard same-domain XHR you are so familiar with.
这就是 CORS 请求了!假定服务器合理的配置了响应 CORS 请求,你的
onload事件处理程序将会触发响应,就像你熟悉的标准的同域 XHR 一样。
End-to-End Example | 端对端示例
Here is a full working sample of a CORS request. Run the sample and watch the network requests in the browser’s debugger to see the actual request being made.
这里有一个 CORS 请求的完整工作示例。运行示例然后在浏览器的调试器中查看网络请求,来看看实际上产生的请求。
Run Sample1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46// Create the XHR object.
function createCORSRequest(method, url) {
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
if ("withCredentials" in xhr) {
// XHR for Chrome/Firefox/Opera/Safari.
xhr.open(method, url, true);
} else if (typeof XDomainRequest != "undefined") {
// XDomainRequest for IE.
xhr = new XDomainRequest();
xhr.open(method, url);
} else {
// CORS not supported.
xhr = null;
}
return xhr;
}
// Helper method to parse the title tag from the response.
function getTitle(text) {
return text.match('<title>(.*)?</title>')[1];
}
// Make the actual CORS request.
function makeCorsRequest() {
// This is a sample server that supports CORS.
var url = 'http://html5rocks-cors.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/index.html';
var xhr = createCORSRequest('GET', url);
if (!xhr) {
alert('CORS not supported');
return;
}
// Response handlers.
xhr.onload = function() {
var text = xhr.responseText;
var title = getTitle(text);
alert('Response from CORS request to ' + url + ': ' + title);
};
xhr.onerror = function() {
alert('Woops, there was an error making the request.');
};
xhr.send();
}
Adding CORS support to the server | 在服务器上增加 CORS 支持
Most of the heavy lifting for CORS is handled between the browser and the server. The browser adds some additional headers, and sometimes makes additional requests, during a CORS request on behalf of the client. These additions are hidden from the client (but can be discovered using a packet analyzer such as Wireshark).
CORS 的大部分繁重工作都是在浏览器和服务器之间进行的。浏览器在代表客户端的 CORS 请求期间添加了一些额外的请求头,有时候 发起额外的请求。这些添加对客户端是隐藏的(但是可以使用诸如 Wireshark 之类的抓包分析工具来发现)。
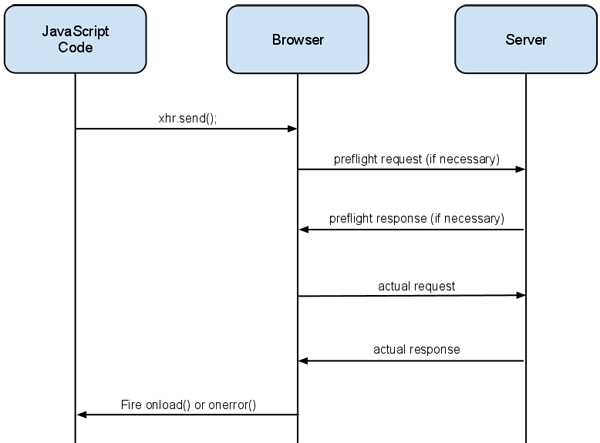 CORS flow
CORS flow
Browser manufacturers are responsible for the browser-side implementation. This section explains how a server can configure its headers to support CORS.
浏览器制造商负责浏览器端的实现。这一节阐述服务器如何配置请求头来支持 CORS。
Types of CORS requests | CORS 请求的类型
Cross-origin requests come in two flavors:
跨源请求主要有2种:
- simple requests 简单请求
“not-so-simple requests” (a term I just made up) 非简单的请求
Simple requests are requests that meet the following criteria:
简单请求必须满足以下准则:
HTTP Method matches (case-sensitive) one of:
HTTP 方法匹配(大小写敏感)下面一种
- HEAD
- GET
- POST
HTTP Headers matches (case-insensitive):
HTTP 请求头匹配(大小写敏感):
- Accept
- Accept-Language
- Content-Language
- Last-Event-ID
- Content-Type, but only if the value is one of:
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- multipart/form-data
- text/plain
Simple requests are characterized as such because they can already be made from a browser without using CORS. For example, a JSON-P request can issue a cross-domain GET request. Or HTML could be used to do a form POST.
简单请求具有这样的特点是因为他们已经可以在不使用 CORS 的情况下浏览器中生成。例如,
JSON-P请求可以发出跨域 GET 请求。或者 HTML 可以用于执行表单 POST。
Any request that does not meet the criteria above is a not-so-simple request, and requires a little extra communication between the browser and the server (called a preflight request), which we’ll get into below.
任何不满足以上准则的请求都是 非简单的 请求,需要在浏览器和服务器之间进行一点点额外的通信(称为 预检请求),我们会在下面介绍。
Handling a simple request | 处理一个简单请求
Lets start by examining a simple request from the client. The table below shows the JavaScript code for a simple GET request on the left, along with the actual HTTP request that the browser emits; CORS specific headers are in bold.
让我们从检查客户端的简单请求开始。下表展示了左侧简单请求的 JavaScript 代码,以及浏览器发出的实际 HTTP 请求;CORS 特定请求头用粗体显示。
JavaScript:1
2
3var url = 'http://api.alice.com/cors';
var xhr = createCORSRequest('GET', url);
xhr.send();
HTTP Request:1
2
3
4
5
6GET /cors HTTP/1.1
Origin: http://api.bob.com
Host: api.alice.com
Accept-Language: en-US
Connection: keep-alive
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0...
The first thing to note is that a valid CORS request always contains an Origin header. This Origin header is added by the browser, and can not be controlled by the user. The value of this header is the scheme (e.g. http), domain (e.g. bob.com) and port (included only if it is not a default port, e.g. 81) from which the request originates; for example: http://api.alice.com.
第一个要注意的地方是,一个可用的 CORS 请求 始终 包含一个 Origin 请求头。这个 Origin 请求头是浏览器添加的,不能被用户控制。这个请求头的值是请求源自的方案(例如:http),域(例如:bob.com),和端口(仅在它不是默认端口时才需要声明 例如:81);例如:http://api.alice.com。
The presence of the Origin header does not necessarily mean that the request is a cross-origin request. While all cross-origin requests will contain an Origin header, some same-origin requests might have one as well. For example, Firefox doesn’t include an Origin header on same-origin requests. But Chrome and Safari include an Origin header on same-origin POST/PUT/DELETE requests (same-origin GET requests will not have an Origin header). Here is an example of a same-origin request with an Origin header:
Origin请求头的出现并不一定意味着这个请求就是跨源请求。所有的跨源请求都要包含 Origin 请求头,一些同源请求也可能会有一个 Origin 请求头。例如,Firefox 在同源请求下不包含 Origin 请求头。但是 Chrome 和 Safari在同源的 POST/PUT/DELETE(同源的 GET 请求不包含 Origin 请求头)请求中会包含一个 Origin 请求头。这是一个有 Origin 请求头的同源请求。
HTTP Request:1
2
3POST /cors HTTP/1.1
Origin: http://api.bob.com
Host: api.bob.com
The good news is that browsers don’t expect CORS response headers on same-origin requests. The response to a same-origin request is sent to user, regardless of whether it has CORS headers or not. However, if your server code returns an error if the Origin doesn’t match a list of allowed domains, be sure to include the origin the request comes from.
好消息是浏览器不希望同源请求上使用 CORS 响应头。同源请求的响应被发送给用户,不考虑它是否包含 CORS 响应头。但是,如果你的服务器代码在 Origin 与允许的域名列表不匹配时返回错误,请确认包含请求来源。
Here’s a valid server response; the CORS-specific headers are bolded
这里是一个有效的服务器响应;CORS 特定的请求头加黑显示了。
HTTP Response:1
2
3
4Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://api.bob.com
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
Access-Control-Expose-Headers: FooBar
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
All CORS related headers are prefixed with “Access-Control-“. Here’s some more details about each header.
所有 CORS 有关的请求头都是以 “Access-Control-” 为前缀的。下面有一些关于每个请求头的详细描述。
Access-Control-Allow-Origin (required) - This header must be included in all valid CORS responses; omitting the header will cause the CORS request to fail. The value of the header can either echo the Origin request header (as in the example above), or be a ‘‘ to allow requests from any origin. If you’d like any site to be able to access your data, using ‘‘ is fine. But if you’d like finer control over who can access your data, use an actual value in the header.
Access-Control-Allow-Origin(必须的)- 这个请求头必须包含在所有有效的 CORS 响应中;忽略这个请求头会导致 CORS 请求失败。这个请求头的值要么回显 Origin 请求头(如上面的例子所示),要么为''(空字符)表示允许来自任何来源的请求。如果你想要任何网站都能够获取你的数据,使用''就可以了。但是如果你希望更好地控制谁可以访问你的数据,就要在请求头设置实际的值。
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials (optional) - By default, cookies are not included in CORS requests. Use this header to indicate that cookies should be included in CORS requests. The only valid value for this header is true (all lowercase). If you don’t need cookies, don’t include this header (rather than setting its value to false).
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials(可选) - 默认情况下,cookie 缓存不被包含在 CORS 请求中。用这个请求头来指示 cookie 缓存要被添加在 CORS 请求中。这个请求头唯一的有效值就是true(允许小写)。如果你不需要 cookie 缓存,就不要包含这个请求头(而不是将请求头的值设置为false)。
The Access-Control-Allow-Credentials header works in conjunction with the withCredentials property on the XMLHttpRequest 2 object. Both these properties must be set to true in order for the CORS request to succeed. If .withCredentials is true, but there is no Access-Control-Allow-Credentialsheader, the request will fail (and vice versa).
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials请求头在XMLHtmlRequest2对象上的 withCredentials 属性 一起使用。这两个属性都要被设置为ture才能让 CORS 请求成功执行。如果.withCredentials为true而没有Access-Control-Allow-Credentials请求头,请求将会失败(反之亦然)。
Its recommended that you don’t set this header unless you are sure you want cookies to be included in CORS requests.
除非你确定需要在 CORS 请求中包含 cookie 缓存,否则不建议设置这个请求头。
Access-Control-Expose-Headers (optional) - The XMLHttpRequest 2 object has a getResponseHeader() method that returns the value of a particular response header. During a CORS request, the getResponseHeader() method can only access simple response headers. Simple response headers are defined as follows:
Access-Control-Expose-Headers(可选) -XMLHttpRequest2对象有一个getResponseHeader()方法,返回一个特定的响应头的值。在 CORS 请求期间 ,getResponseHeader()方法只能访问简单的响应头。简单的响应头定义如下:
- Cache-Control
- Content-Language
- Content-Type
- Expires
- Last-Modified
- Pragma
If you want clients to be able to access other headers, you have to use the Access-Control-Expose-Headers header. The value of this header is a comma-delimited list of response headers you want to expose to the client.
如果想要客户端访问其他请求头,必须使用
Access-Control-Expose-Headers请求头。这个请求头的值是你想要向客户端公开的响应头部的逗号分隔列表。
Handling a not-so-simple request | 处理一个 非简单的 请求
So that takes care of a simple GET request, but what if you want to do something more? Maybe you want to support other HTTP verbs like PUT or DELETE, or you want to support JSON using Content-Type: application/json. Then you need to handle what we’re calling a not-so-simple request.
这样就可以处理一个简单请求了,但是如果你想要做更多事情呢?可能你想支持其他诸如
PUT或者DELETE之类的HTTP谓词,或者你想用Content-Type:application/json来支持JSON格式的响应。那么你就需要处理我们所谓的非简单的请求了
A not-so-simple request looks like a single request to the client, but it actually consists of two requests under the hood. The browser first issues a preflight request, which is like asking the server for permission to make the actual request. Once permissions have been granted, the browser makes the actual request. The browser handles the details of these two requests transparently. The preflight response can also be cached so that it is not issued on every request.
一个
非简单的请求在客户端看来就像一个单个请求,但是它实际上包含两个请求。浏览器首先发起一个预检请求,看起来像是向服务器申请发起实际请求的权限。一旦权限被赋予,浏览器就会发起真正的请求了。浏览器处理这两个请求的详细过程是透明的。预检请求的响应也可以被缓存起来,这样就不用在每次请求的时候都发起预检请求了。
Here’s an example of a not-so-simple request:
这里有一个
非简单的请求的示例:
JavaScript:1
2
3
4
5var url = 'http://api.alice.com/cors';
var xhr = createCORSRequest('PUT', url);
xhr.setRequestHeader(
'X-Custom-Header', 'value');
xhr.send();
Preflight Request:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8OPTIONS /cors HTTP/1.1
Origin: http://api.bob.com
Access-Control-Request-Method: PUT
Access-Control-Request-Headers: X-Custom-Header
Host: api.alice.com
Accept-Language: en-US
Connection: keep-alive
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0...
Like the simple request, the browser adds the Origin header to every request, including the preflight. The preflight request is made as an HTTP OPTIONS request (so be sure your server is able to respond to this method). It also contains a few additional headers:
和简单请求类似,浏览器会向每一个请求添加 Origin 请求头,包括预检请求。这个预检请求是作为
HTTP OPTIONS请求生成的(因此要确保你的服务器能够响应这种方式)。它也会包含额外一些请求头:
Access-Control-Request-Method - The HTTP method of the actual request. This request header is always included, even if the HTTP method is a simple HTTP method as defined earlier (GET, POST, HEAD).
Access-Control-Request-Method- 实际请求的 HTTP 方法。即使 HTTP 方法是前面定义过的简单 HTTP 方法(GET,POST,HEAD),也始终包含这个请求头。
Access-Control-Request-Headers - A comma-delimited list of non-simple headers that are included in the request.
Access-Control-Request-Headers- 包含在请求中的一个非简单请求头逗号分隔列表。
The preflight request is a way of asking permissions for the actual request, before making the actual request. The server should inspect the two headers above to verify that both the HTTP method and the requested headers are valid and accepted.
在进行实际请求之前,预检请求是一种询问实际请求权限的方法。 服务器应该检查上面两个请求头以验证 HTTP 方法和请求头有效并接受。
If the HTTP method and headers are valid, the server should respond with the following:
如果 HTTP 方法和请求头有效,服务器应该返回如下响应:
Preflight Request:
预检请求:
1 | OPTIONS /cors HTTP/1.1 |
Preflight Response:1
2
3
4Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://api.bob.com
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, POST, PUT
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: X-Custom-Header
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Access-Control-Allow-Origin (required) - Like the simple response, the preflight response must include this header.
Access-Control-Allow-Origin(必须)- 像简单响应,预检响应也必须包含这个响应头部。
Access-Control-Allow-Methods (required) - Comma-delimited list of the supported HTTP methods. Note that although the preflight request only asks permisions for a single HTTP method, this reponse header can include the list of all supported HTTP methods. This is helpful because the preflight response may be cached, so a single preflight response can contain details about multiple request types.
Access-Control-Allow-Methods(必须) - 受支持的 HTTP方法的逗号分隔列表。要注意虽然预检请求只会询问单个简单 HTTP 请求的权限,但是这个响应头可以包含所有支持的 HTTP 方法。这很有用,因为可以缓存预检 请求响应,所以一个单个预检响应可以包含多种请求类型的详细信息。
Access-Control-Allow-Headers (required if the request has an Access-Control-Request-Headers header) - Comma-delimited list of the supported request headers. Like the Access-Control-Allow-Methods header above, this can list all the headers supported by the server (not only the headers requested in the preflight request).
Access-Control-Allow-Headers(在请求包含一个Access-Control-Request-Headers的情况下是必须的) - 受支持的请求头的逗号分隔列表。像上面的Access-Control-Allow-Methods,这可以列出所有被服务器支持的请求头(不仅是预检请求中请求的标头)。
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials (optional) - Same as simple request.
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials(可选) - 与简单请求相同。
Access-Control-Max-Age (optional) - Making a preflight request on every request becomes expensive, since the browser is making two requests for every client request. The value of this header allows the preflight response to be cached for a specified number of seconds.
Access-Control-Max-Age(可选) - 对每个请求都进行预检请求是开销很大的,因为浏览器要为每次客户端请求发起两次请求。这个请求头的值允许预检请求的响应被缓存指定秒数的时间。
Once the preflight request gives permissions, the browser makes the actual request. The actual request looks like the simple request, and the response should be processed in the same way:
一点预检请求提供了权限,浏览器就会发起实际请求。实际请求看上去就像简单请求,请求的响应也是用相同的方式处理:
Actual Request:1
2
3
4
5
6
7PUT /cors HTTP/1.1
Origin: http://api.bob.com
Host: api.alice.com
X-Custom-Header: value
Accept-Language: en-US
Connection: keep-alive
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0...
Actual Response:1
2Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://api.bob.com
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
If the server wants to deny the CORS request, it can just return a generic response (like HTTP 200), without any CORS header. The server may want to deny the request if the HTTP method or headers requested in the preflight are not valid. Since there are no CORS-specific headers in the response, the browser assumes the request is invalid, and doesn’t make the actual request:
如果服务器想要拒绝 CORS 请求,它只能返回通用响应(如 HTTP 200),而不需要任何 CORS 头。如果 HTTP 方法或者预检请求的请求头无效,服务器可能会拒绝请求。因为返回中没有 CORS 特定的响应头,浏览器会假定请求不可用,就不会发起实际请求了。
Preflight Request:
预检请求
1 | OPTIONS /cors HTTP/1.1 |
Preflight Response:
预检响应
1 | // ERROR - No CORS headers, this is an invalid request! |
If there is an error in the CORS request, the browser will fire the client’s onerror event handler. It will also print the following error to the console log:
如果 CORS 请求发生了错误,浏览器会触发客户端的
onerror事件处理程序。也会在控制台日志中打印如下错误:
1 | XMLHttpRequest cannot load http://api.alice.com. Origin http://api.bob.com is not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Origin. |
The browser doesn’t give you a lot of details on why the error occurred, it only tells you that something went wrong.
浏览器不会给出为什么出错的详细信息,它只会告诉你出错了。
A word about security | 谈一点安全
While CORS lays the groundwork for making cross-domain requests, the CORS headers are not a substitute for sound security practices. You shouldn’t rely on the CORS header for securing resources on your site. Use the CORS headers to give the browser directions on cross-domain access, but use some other security mechanism, such as cookies or OAuth2, if you need additional security restrictions on your content.
虽然 CORS 为跨域请求奠定了基础,但是 CORS 请求头不能代替健全的安全措施。你不能依赖 CORS 头来保障网站资源的安全。使用 CORS 头来给浏览器执行跨域访问的指导,但是如果想要你的内容更加安全,使用其他的安全机制,例如 cookies 或者 OAuth2 。
CORS from JQuery | 用 JQuery CORS
JQuery’s $.ajax() method can be used to make both regular XHR and CORS requests. A few notes about JQuery’s implementation:
JQuery 的 $.ajax() 方法可以用来发起常规 XHR 和 CORS 请求。JQuery 实现的一些注意事项:
JQuery’s CORS implementation doesn’t support IE’s XDomainRequest object. But there are JQuery plugins that enable this. See http://bugs.jquery.com/ticket/8283 for details.
JQuery 的 CORS 实现不支持 IE 浏览器的
XDomainRequest对象。但是有 JQuery 的插件使它支持。这里查看详情。The
$.support.corsboolean will be set totrueif the browser supports CORS (This returnsfalsein IE, see bullet above). This can be a quick way to check for CORS support.如果浏览器支持 CORS ,布尔值
$.support.cors将被设置为true(在 IE 浏览器下返回false,看上面的说明)。这是检查 CORS 支持的一个快捷方法。Here’s sample code for making a CORS request with JQuery. The comments give more details on how certain properties interact with CORS.
这里有一份用 JQuery 发起 CORS 请求的示例代码。注释部分详细的描述了具体每个属性是如何与 CORS 交互的。
1 | $.ajax({ |
Cross-Domain from Chrome Extensions | 用Chrome扩展跨域
Chrome extensions support cross-domain requests in a two different ways:
Chrome 浏览器扩展通过下面两种方式支持跨域请求:
Include domain in manifest.json - Chrome extensions can make cross-domain requests to any domain if the domain is included in the “permissions” section of the manifest.json file:
在
manifest.json中包含域名 - 如果域名包含在 manifest.json 文件中的 “permission” 区域中,Chrome 浏览器扩展可以生成跨域请求到任意域名。1
"permissions": [ "http://*.html5rocks.com"]
The server doesn’t need to include any additional CORS headers or do any more work in order for the request to succeed.
服务器不需要包含任何额外的 CORS 头,也不需要做其他更多事情来让请求成功。
CORS request - If the domain is not in the manifest.json file, then the Chrome extension makes a standard CORS request. The value of the Origin header is “chrome-extension://[CHROME EXTENSION ID]”. This means requests from Chrome extensions are subject to the same CORS rules described in this article.
CORS 请求 - 如果域名不在 manifest.json 文件中,Chrome 浏览器扩展就会发起一个标准的 CORS 请求。Origin 头的值为 “chrome-extension://[CHROME EXTENSION ID]”。这意味着 Chrome 浏览器扩展发出的请求必须遵循本文叙述的相同的 CORS 规则。
Known Issues | 已知问题
CORS support is still being actively developed in all browsers; here’s a list of known issues (as of 10/2/2013):
CORS 支持仍然在所有浏览器中活跃的开发;这里有一个已知问题列表(截至 10/2/2013)
FIXED
XMLHttpRequests’ getAllResponseHeaders() doesn’t honor Access-Control-Expose-Headers - Firefox doesn’t return response headers when calling getAllResponseHeaders(). (Firefox bug). A similar bug in WebKit has been fixed.以解决:XMLHttpRequest 的 getAllResponsHeader() 不支持 Access-Control-Expose_Headers - 当调用getAllResponseHeaders() 时Firefox浏览器不返回响应头。(Firefox bug)。WebKit 中同样的问题已经被解决了。
No error information provided to onerror handler - When the onerror handler is fired, the status code is 0, and there is no statusText. This may be by design, but it can be confusing when trying to debug why CORS requests are failing.
onerror 事件处理程序不提供错误信息。当 onerror 处理程序被触发的时候,状态码为0,没有 statusText。这可能是故意的,但是这在调试 CORS 请求错误时会让人非常迷惑。
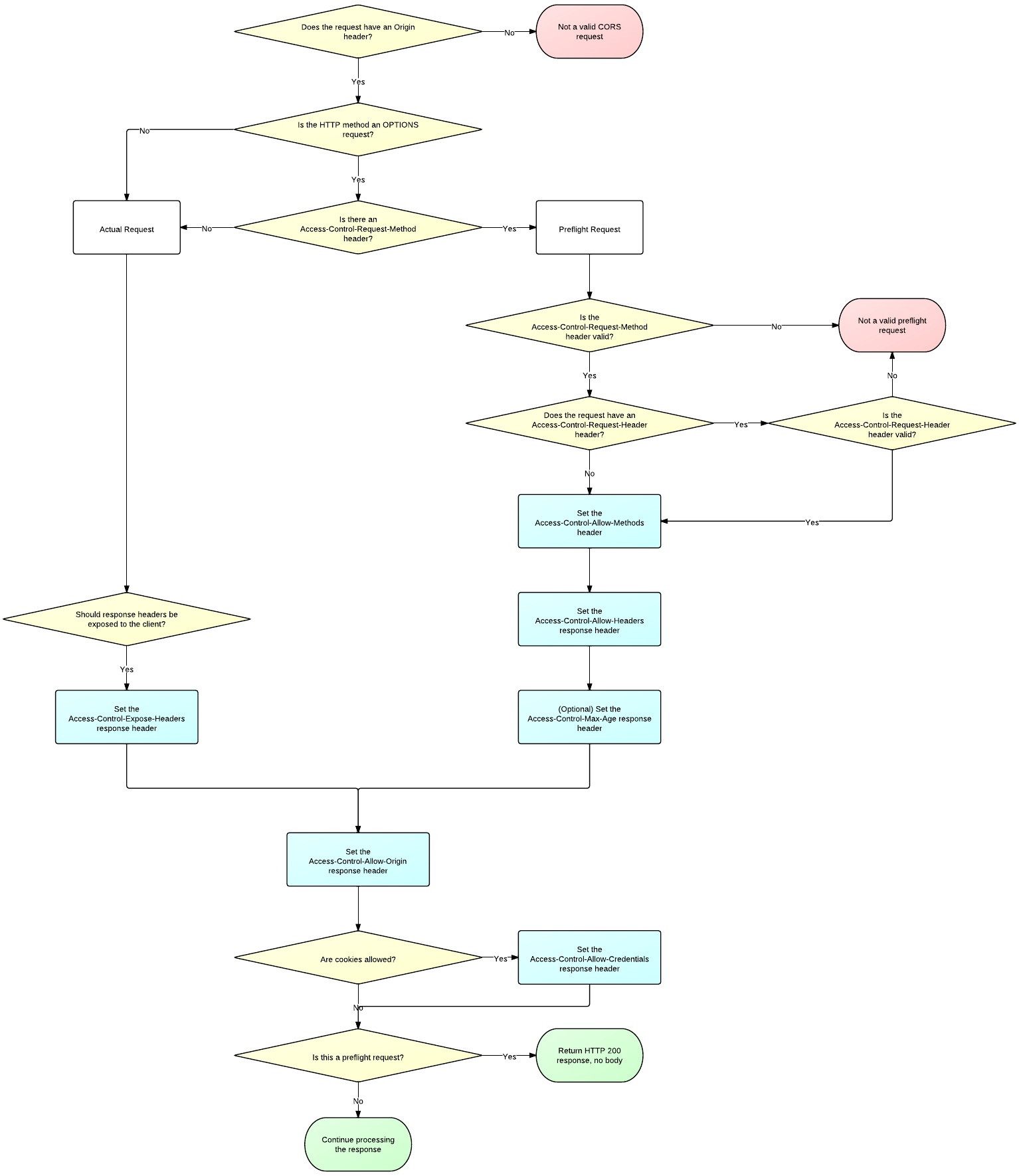
CORS Server Flowchart | CORS 服务器流程图
The flowchart below shows how a server should make the decisions as to which headers to add to a CORS response. Click the image to see a larger version.
下面的流程图展示了服务器应该如何决定将哪些响应头添加到 CORS 响应中。点击查看大图。
CORS w/ Images
In Canvas and WebGL contexts, cross origin images can pose big problems. You can use the crossOrigin attribute on the image element to address much of them. Read Chromium Blog: Using Cross-domain images in WebGLand Mozilla Hacks: Using CORS to load WebGL textures from cross-domain images for the details. Implementation specifics can be found at the MDN page for CORS-enabled Image.
在 Canvas 和 WebGL 环境中,跨源图像可能导致大问题。你可以用图片元素的 crossOrigin 属性来解决大部分的问题。阅读 Chromium Blog: Using Cross-domain images in WebGL 和 Mozilla Hacks: Using CORS to load WebGL textures from cross-domain images 详细了解。在 MDN 页面上可以找到 支持 CORS 图像 的实现细节。
Resources
Here are some resources if you’d like to learn more about CORS:
- The CORS Spec
- A good intro to CORS from Nicholas Zakas
- enable-cors.org - More details on how to enable CORS on your server.